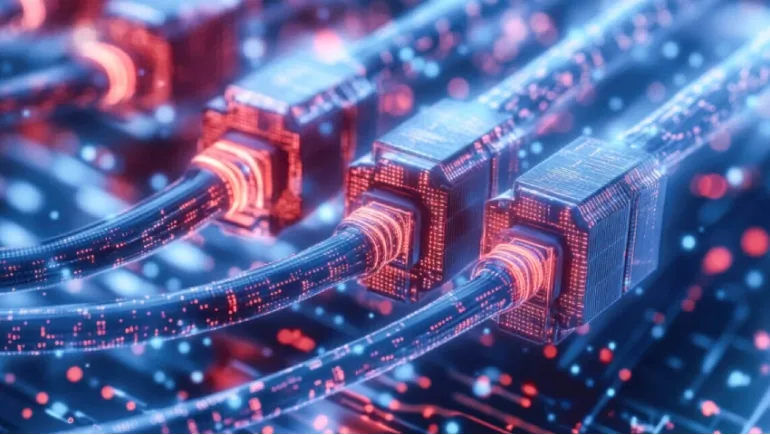
Quantum teleportation has long been an intriguing concept in quantum mechanics, but recent advancements have taken it from theoretical discussions to practical applications. In a groundbreaking achievement, engineers have successfully demonstrated quantum teleportation within active internet cables, setting the stage for a new era of ultra-secure and lightning-fast communication. This milestone is poised to revolutionize quantum networking, cryptography, and global data transfer.
Quantum teleportation is the process of transmitting quantum states from one location to another without physically transferring the actual particle. This feat is achieved through quantum entanglement, where two particles become so intrinsically connected that the state of one instantaneously influences the other, regardless of distance.
Unlike classical data transmission, which relies on electrical or optical signals traveling through cables, quantum teleportation transfers information using entangled qubits, offering an unprecedented level of security and efficiency. The ability to achieve this in active internet cables means that quantum-based communication systems can soon be integrated into existing digital infrastructure, paving the way for a quantum internet.
For the first time, engineers have successfully implemented quantum teleportation over active internet cables spanning hundreds of kilometers. This experiment, conducted in collaboration with leading universities and tech companies, involved sending entangled photons through fiber optic networks, a significant step toward practical quantum communication.
A major challenge in previous quantum teleportation attempts was the loss of quantum coherence due to environmental noise and interference in traditional communication channels. However, recent advancements in quantum repeaters and entanglement purification techniques have improved data fidelity, making it possible to maintain stable entanglement over long distances.
The process of quantum teleportation in active internet cables follows a structured three-step mechanism:
This process ensures that data transmission remains unhackable, as any attempt to intercept or measure the quantum state would disrupt the entanglement, rendering the information useless to eavesdroppers.
The successful implementation of quantum teleportation in active internet cables is a crucial step toward building a quantum internet. This new network architecture would enable ultra-secure communication between financial institutions, government agencies, and even everyday users, making traditional hacking methods obsolete.
Quantum teleportation will also play a vital role in quantum computing by allowing seamless transfer of quantum states between remote quantum processors. This would enable quantum cloud computing, where users can harness the power of distributed quantum computers without requiring direct physical access.
Large-scale data centers can integrate quantum teleportation technology to enhance data security and processing speeds. This will be particularly beneficial for industries dealing with sensitive information, such as healthcare, defense, and finance.
Scientists believe that quantum teleportation could revolutionize space exploration by enabling instantaneous communication between spacecraft and Earth. By implementing quantum entanglement in satellite networks, interplanetary communication could become much more efficient and reliable.
While the recent breakthrough is promising, several challenges need to be addressed before quantum teleportation in internet cables becomes mainstream:
Future research will focus on integrating quantum teleportation into real-world internet infrastructure, with major tech firms and academic institutions investing in the development of quantum-compatible networking equipment.
The successful achievement of quantum teleportation in active internet cables is a landmark moment in modern physics and engineering. This development brings us closer to realizing the vision of a quantum internet, capable of instantaneous, secure data transmission without the vulnerabilities of classical communication methods.










Comments
There are no comments for this Article.